The Value of Garden Crop Rotation
Crop rotation is a fundamental gardening technique that involves gradually changing crops in a specific area. This strategy has been used and recognized for hundreds of years due to its numerous benefits. By implementing crop rotation, gardeners can enhance soil productivity, manage pesky insects and diseases, and overall promote plant health.
Benefits of Crop Rotation
Crop rotation is a process that offers several benefits, including improved soil fertility. Different crops used in rotation require different nutrients, and while some crops can deplete certain nutrients from soil, others can restore them. This balanced approach ensures that the soil remains nutrient-rich, allowing plants to reach their full potential. Additionally, crop rotation helps to reduce soil erosion as it provides a constant amount of ground cover, thereby preventing topsoil erosion.
The prevention of nutrient depletion and the replenishment of nutritional requirements are critical for the sustainability of agriculture. Depending on the nutritional needs of various crops, farmers may choose to alternate them to safeguard soil fertility. Legumes such as peas and soybeans are capable of taking nitrogen from the atmosphere and converting it into a form usable by other plants. This natural process replenishes nitrogen in the soil, which is beneficial for future crops. However, planting nitrogen-depleting crops such as corn and wheat can be offset by interchanging them with other crops that can restore nitrogen to the soil.
Crop rotation not only helps to reduce the spread of soil pests and diseases, but it also keeps them under control. Planting the same crop in a field over successive years creates a favorable environment for pests and diseases to thrive. Crop rotation can disrupt the life cycle of these harmful organisms, preventing their establishment and spread. As a result, there may be a decrease in the usage of fungicides and pesticides, promoting more sustainable and environmentally friendly farming methods. By using different crops with unique nutrient requirements and root structures in rotation, crop rotation can enhance soil quality and composition.
Crop rotation can also improve the soil's quality and its ability to hold water. Alternating crops with deep and shallow roots can enhance the soil's ability to retain water and withstand erosion. Legumes, due to their extensive roots, can penetrate the soil deeply, loosening compacted layers and improving water absorption. In contrast, plants with shallow roots such as leafy greens can hold moisture in the topsoil layers and reduce the amount of water that flows down the surface. The presence of both shallow and deep roots enhances the soil structure, resulting in improved health and resilience. This, in turn, enhances the overall productivity and well-being of the farm.
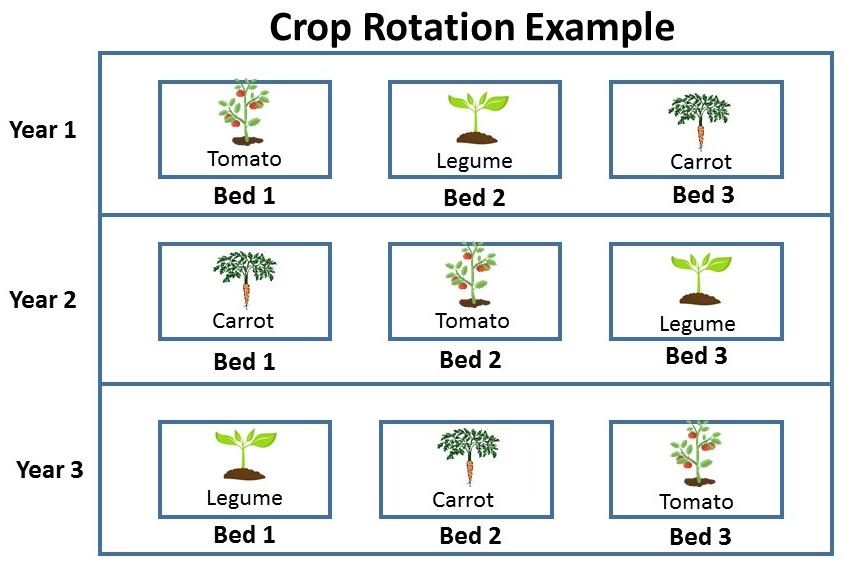
Crop Rotation Techniques
Crop rotation is a traditional technique where plants are rotated in a predetermined sequence. After a cereal crop is harvested, a legume is usually planted, followed by a root crop. This helps to prevent the natural progression of insects and diseases that could focus on a crop, reducing reliance on chemical pesticides. Since various plants need different nutrients, crop rotation helps to balance the nutrients in the soil. Legumes, for example, capture nitrogen from the atmosphere and resupply the soil with this essential ingredient, ensuring its accessibility for future plant growth.
Sequential rotation of several plant families enhances soil structure and minimizes soil erosion. The soil is consistently aerated and compacted by the rotation of crops with shallow and deep roots to boost water infiltration and drainage. Monoculture systems usually face problems such as waterlogging and soil compaction, which can be prevented by employing this method. Furthermore, crop rotation can interfere with the natural habitats of weeds and pests, affecting their ability to reproduce and flourish in the field. This organic and natural pest control method can promote environmentally friendly and sustainable farming by reducing reliance on chemical pesticides and herbicides.
Using a crop rotation schedule with a span of three years can improve the quality and output of vegetable soil. Farmers can intentionally alternate the growing of crops on a year-round basis by dividing the field into three sections, where each area is devoted to growing a different crop. This interference with the natural progression of pests and diseases that could focus on a crop may reduce the need for chemical treatments. Rotation of crops regularly replenishes the essential nutrients in the soil, reducing the need for synthetic fertilizers. Different crops require different nutrients, hence the need for crop rotation.
Another important technique for sustainable agriculture is cover cropping. Cover crops are advantageous to a soil surface during times when cash crops aren't being developed, as they provide the soil with a cushioning layer. These crops keep the soil from drooping and keep it moist after a heavy rain. Additionally, they improve the soil structure and increase the amount of organic material available for absorbing nutrients and retaining water. The use of heavy labor and costly herbicides is also reduced since cover crops naturally manage weeds.
In sustainable farming, it's common to grow cover crops during the fallow period. Fields aren't planted for business uses, and fallow times are when no plants are planted; they are left empty. At this time, cover crops are sown to guard the soil's health and keep it from depreciating or exhausting. A cover crop provides farmers the chance to improve their farming practices, and the benefits go beyond the obvious.
Cover crops offer numerous benefits, such as improving soil structure, increasing organic matter, enhancing nutrient cycle, and reducing erosion. By competing for space, nutrients, and light with weeds, cover crops impede their growth. They also attract beneficial insects and provide a good environment for pollinators, thereby promoting diversity on the farm. Incorporating cover crops into agricultural practices promotes resilience and sustainability, as well as improving soil health and weed management.
Another sustainable farming approach is intercropping, where two or more crops are planted close to each other. This strategy optimizes land use and enhances farm diversity. Intercropping reduces reliance on chemical pesticides and protects plants from pests and diseases. Growing different crops with different root systems and nutrient needs improves soil quality and nutrient circulation, creating a harmonious ecosystem and a robust soil microbiome.
Complementary crops can be grown simultaneously to improve water and nutrient efficiency. Certain plants have extensive root systems that pull nutrients from the topsoil, while others have shallow roots that tap into deeper soil for water and nutrients. By intercropping compatible crops, farmers can optimize resource consumption, minimizing water and fertilizer wastage and improving farm productivity while preserving natural resources. Intercropping also promotes advantageous associations among plants, such as leguminous crops that fix nitrogen, leading to improved soil fertility and reduced dependence on synthetic fertilizers.
Intercropping enhances yields and pest control by lowering pest populations through companion planting. Farmers can intentionally plant certain crops to reduce their reliance on chemical pesticides and promote sustainable and nutritive agricultural techniques. Intercropping promotes a crucial balance between helpful insects and predators, which is important for successful pest management. Diverse plants can mutually benefit one another through their development patterns and nutrient needs, enhancing overall efficiency and production of the farm by optimizing resource and space use.
Practical Tips for Crop Rotation
Before developing the layout of your garden, it's important to have a great crop rotation method in place. Farmers meticulously organize the different sections of the garden to ensure the right rotation and lay out the correct plots for each crop. This technique prevents the spread of diseases and pests while allowing for efficient management of soil fertility and nitrogen. Planning crop rotations based on the different growth cycles and maturation times of plants is crucial, while considering the timing of these cycles. This way, you can ensure a consistent supply of fresh vegetables throughout the growing season and maximize the usage of your limited space.
Crops can be divided into groups based on their family and the order in which they are rotated to better the rotation. Groupings of plant families are used to recognize and manage pest and disease problems that might influence certain plant families. By systematically rotating crops, pests can be disrupted in their life cycles, and their populations can be reduced. To do this, it is possible to alternate between plants that are resistant to certain pests and plants that don't attract these pests. Farmers can improve the health and productivity of their crops by applying crop rotation methods, thus strengthening the overall sustainability of agricultural systems.
Crop rotation can be further improved by companion planting. Companion planting is the practice of taking care of several plants in close proximity to one another with the aim of benefiting from their mutually useful qualities. Some plants have the ability to ward off pests that invade neighboring crops, while other plants can attract beneficial insects that feed on insects. By deliberately choosing plants that complement each other, farmers can maintain a balance and strengthen the ecosystem within their fields. This decreases the usage of chemical pesticides, improves soil fertility, and promotes natural pest management.
Using crop rotation in gardens will ultimately improve the benefits of companion planting. By rotating crops due to their various nutrient requirements and ability to disrupt pest cycles, diseases and pests can be kept from developing in the soil. The soil structure is enhanced, and fertility is increased because different crops are added in various quantities to the soil. Using crop rotation and companion planting techniques can lead to more environmentally friendly and sustainable farming practices, which improve farmer productivity. In a nutshell, by putting into action crop rotation and companion planting strategies, farmers can improve the health and productivity of their crops and strengthen the overall sustainability of agricultural systems.
Links:
No comments:
Post a Comment